The Year 536
March 18, 2019
There's hardly a week that passes without news of some major
natural disaster. These can be extended events, such a
droughts, or quick insults such as
floods,
earthquakes,
hurricanes,
tornadoes or
tsunamis. While
humans think that we are
masters of all we survey, such natural disasters remind us that we exist on this
planet only at the
whim of
Nature. Fortunately, these natural disasters affect small regions of the
Earth, only, and none threaten all of mankind at once as did the flood in the
Biblical story of
Noah's Ark.
Noah's
near-extinction level flood might be an embellished description of an
historical flood. There are many stories of such a flood in
ancient literature; and, just as in Noah's scheme of saving
animal species on an
ark, these all explain how the Earth was repopulated. The
Babylonian account of a great flood in the
Gilgamesh epic tells of a man,
Utnapishtim, who was instructed by his
god to build an ark that also carried saved animal species.

Clay tablet no. XI of the Epic of Gilgamesh in which the flood myth is inscribed.
As the epic tells, "A stupor of despair went up to heaven when the god of the storm turned daylight to darkness, when he smashed the land like a cup. One whole day the tempest raged, gathering fury as it went, it poured over the people like the tides of battle..."[1]
(British Museum reference K.3375, via Wikimedia Commons)
While Noah's ark was
rectangular and Noah's flood lasted 40 days and nights, Utnapishtim's ark was
square and his flood lasted just six days and seven nights. Some of Noah's flood waters came from the Earth ("fountains of the deep"), but all of Utnapishtim's water was from
rain. Among the similarities in the two tales is that a release of
birds was used to find
land, and each ark came to rest on a
mountain, Noah's on
Ararat and Utnapishtim's on
Nisir.
The
ancient Greeks had their own flood story in the tale of
Deucalion and
Pyrrha, mentioned by
Plato (c.428 BC-c.348 BC) in his
Timaeus but fully told by
Ovid in his
Metamorphoses. Plato places the flood at the end of the
Bronze Age, and Deucalion built an ark to carry himself and his
wife, Pyrrha, for nine days and nights until the ark landed atop
Mount Parnassus. An
oracle of the
goddess,
Themis, told him a method to repopulate the world. He was to throw the
bones of his
mother behind him. In this case, the mother was
Mother Earth, and her bones were
rocks. Deucalion's rocks transformed into
men, and Pyrrha's rocks transformed into
women, a very
efficienct abiogenesis.
Such repeated telling of the flood tale indicates that a natural calamity might have happened in
prehistoric times. One
theory is that the
eruption of Thera (c. 1600 BC) might have caused a tsunami in the
Mediterranean Sea. Another theory is that a
meteor or
comet impacted the
Indian Ocean around 3000-2800 BC with the creation the 19
mile diameter (30
kilometer)
Burckle Crater that also generated a huge tsunami. Three thousand years is not that distant in time, and
modern humans were present. This event alone justifies the idea that we should be serious about
detection and mitigation of potentially deadly asteroids, a topic that I wrote about in an
earlier article (Asteroid Deflection, April 19, 2012).

Invader from space.
This is an artist's illustration of a suspected asteroid impact off the northwestern coast of Australia that left a 125 mile diameter crater and caused massive extinctions about 250 million years ago.
There's a YouTube compilation of a 570 kilogram meteor strike at Lake Chebarkul, Russia, on February 15, 2013, that shows the power of a meteor of this small size.[2]
(NASA image, Continental Dynamics Workshop/NSF.)
A recent
article in
Science announced the discovery of an
impact crater, hidden beneath the
Greenland Ice Sheet, by a huge international team of
scientists.[3-4] The impact was not that long ago, during a time when modern humans were present. Members of the
research team were from the
University of Copenhagen (Copenhagen, Denmark),
Aarhus University (Aarhus, Denmark), the
Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (Bremerhaven, Germany), the
University of California, Irvine (Irvine, California),
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (Pasadena, California), the
University of Bremen (Bremen, Germany), the
University of Alaska Fairbanks (Fairbanks, Alaska), the
Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (Copenhagen, Denmark), the
Maine Mineral and Gem Museum (Bethel, Maryland), the
University of Ottawa (Ottawa, Canada), the
Technical University of Denmark (Kongens Lyngby, Denmark), the
University of Fribourg (Fribourg, Switzerland), the
University of Zurich (Zurich, Switzerland),
Cardiff University (Cardiff, UK), the
Université Grenoble Alpes (Grenoble, France), the
University of Kansas (Lawrence, Kansas), the
University of Cambridge (Cambridge, UK), the
Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (Cambridgeshire, UK), and the
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (Greenbelt, Maryland).[3]
This 31-kilometer diameter impact crater is located beneath
Hiawatha Glacier in
northwest Greenland, and it's evidenced by a
circular bedrock depression.[3-4] It was discovered just now because of Greenland's ice cover and remote location.[3] The crater was apparently caused by a 1.5-kilometer
asteroid, thereby producing one of Earth's 25 largest-known craters.[4] The impact is dated at about 13,000 years ago when
mammoths were in decline and humans were populating
North America.[4]
Geochemical analysis of glacial
sediment indicates that the meteor was an
iron asteroid.[3]
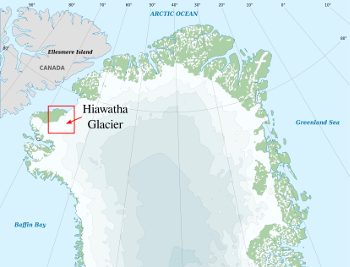
A map of northern Greenland marking the location of Hiawatha Glacier where the impact crater was discovered.
This impact event happened just 13,000 years ago, and it acts as another warning sign that we should make a survey of potential impactors.
(Wikimedia Commons image by Eric Gaba (modified). Click for larger image.)
The
Solar System was a
chaotic place in its early
history, but there's a possibility that things are winding-down and fewer impact events can be expected. This
optimistic conjecture has been disproved by recent work that shows that the impact rate has actually increased, by a factor of 2.6, about 290 million years ago.[5-6] While
erosion on Earth has obliterated the record of many impact events, the
Moon has been subjected to the same impact history, so it's crater record should parallel that of Earth.[6] The lunar crater record was examined using data from the
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.[6]
While there have been no major meteor impacts in recent history (the 1908
Tunguska event that released the equivalent
energy of several tens of
megatons of TNT was large, but had only local effect), there are other natural cataclysms that have had global affect. The 1883
eruption of the
Krakatoa volcano is one example. The
explosion was heard up to 3,000 miles away, and its
pressure wave was intense enough to circle the globe three and a half times. The
volcanic ash caused the average global
temperature to fall by more than 1
°C in the subsequent year, and
weather patterns were disrupted for five years.

The "afterglow" of the 1883 Krakatoa eruption, as published by the Royal Society of Great Britain Krakatoa Committee. (Illustration from "The eruption of Krakatoa, and subsequent phenomena," 1888, George James Symonds, Ed., Item 71-1250 from the Houghton Library, Harvard University, via Wikimedia Commons.)
As
chronicled by various historical sources, there was a more extreme weather event in the
6th century,
starting around the years 535-536, that's now been shown by
scientific study to have a volcanic origin.[7-9] As
Byzantine historian,
Procopius (c.500 - c.554), wrote in his
History of the Wars, Book IV, Chapter XIV,
For the Sun gave forth its light without brightness, like the Moon, during this whole year, and it seemed exceedingly like the Sun in eclipse, for the beams it shed were not clear nor such as it is accustomed to shed.
Europe, the
Middle East, and parts of
Asia were blanketed by a
mysterious fog for 18 months, and
tree ring studies, a traditional
climate-tracking method, revealed that the years around 540 were unusually cold.[8-9]
Summer temperatures in 536 were 1.5°C to 2.5°C lower, and this was the start of the coldest
decade in the past 2300 years.[8-9] This unusual weather was quickly followed by a
bubonic plague called the
Plague of Justinian in 541 in which about half the
population perished. This plague hastened the demise of the
Roman Empire.[8-9]
Paul Mayewski and his
colleagues at the
Climate Change Institute of the
University of Maine (Orono, Maine) have analyzed
volcanic glass particles in an
ice core drilled in 2013 in the
Colle Gnifetti Glacier in the
Swiss Alps.[9] This 72
meter length core contains more than 2000 years of
atmospheric sediments.[9] Using
elemental analysis by x ray excitation (XPS) they found evidence for a cataclysmic volcanic eruption early in 536.[7] Chemical similarities points to
Iceland as a likely source.[8]
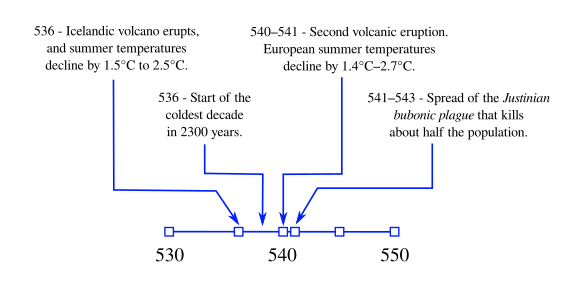
Timeline of events from 530-550. The eruption of an Icelandic volcano in 536 led to decreased insolation, cooler weather, crop failure, and a plague. (Created using Inkscape from data in refs. 7-9.[7-9] Click for larger image.)
The ice core analysis showed that the 536 eruption was followed by two others, in 540 and 547.
Society appears to have recovered by 640 when traces of
lead indicate
silver smelting.[8] The ice core data shows that silver smelting stopped at the time of the
Black Death from 1349 to 1353.[8] I wrote about the Black Death in an
earlier article(Yersinia pestis, February 1, 2016).
References:
- N. K. Sanders, "The Epic of Gilgamesh," Books Online, Assyrian International News Agency (www.aina.org).
- Meteor Hits Russia Feb 15, 2013 - Event Archive, YouTube Video by Tuvix72, February 18, 2013.
- Kurt H. Kjaer, Nicolaj K. Larsen, Tobias Binder, Anders A. Bjørk, Olaf Eisen, Mark A. Fahnestock, Svend Funder, Adam A. Garde, Henning Haack, Veit Helm, Michael Houmark-Nielsen, Kristian K. Kjeldsen, Shfaqat A. Khan, Horst Machguth4, Iain McDonald, Mathieu Morlighem, Jérémie Mouginot, John D. Paden, Tod E. Waight, Christian Weikusat, Eske Willerslev1. and Joseph A. MacGregor, "A large impact crater beneath Hiawatha Glacier in northwest Greenland," Science Advances, vol. 4, no. 11 (November 14, 2018), Article no. eaar8173, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aar8173.
- Paul Voosen, "Ice age impact," Science, vol. 362, no. 6416 (November 16, 2018), pp. 738-742, DOI: 10.1126/science.362.6416.738.
- Sara Mazrouei, Rebecca R. Ghent, William F. Bottke, Alex H. Parker, and Thomas M. Gernon, "Earth and Moon impact flux increased at the end of the Paleozoic," Science, vol. 363, no. 6424 (January 18, 2019), pp. 253-257, DOI: 10.1126/science.aar4058.
- Christian Koeberl, "When Earth got pummeled," Science, vol. 363, no. 6424 (January 18, 2019), pp. 224-225, DOI: 10.1126/science.aav8480.
- Ann Gibbons, "Eruption made 536 'the worst year to be alive'," Science, vol. 362, no. 6416 (November 16, 2018), pp. 733-734, DOI: 10.1126/science.362.6416.733.
- Ann Gibbons, "Why 536 was 'the worst year to be alive'," Science (November 15, 2018), doi:10.1126/science.aaw0632.
- Ultra-Precise Ice Core Sampling and the Explosive Cause of the Dark Ages – Mayewski & Kurbatov, University of Maine Climate Change News, December 18, 2018.
Linked Keywords: Natural disaster; drought; flood; earthquake; tropical cyclone; hurricane; tornado; tsunami; human; masters of all we survey; planet; whim; Nature; Earth; Bible; Biblical; Noah's Ark; extinction event; near-extinction level; flood myth; historical flood; ancient literature; animal; species; ark; Babylon; Babylonian; Gilgamesh flood myth; Gilgamesh epic; Utnapishtim; deity; god; clay tablet; British Museum; rectangle; rectangular; square; rain; bird; continent; land; mountain; Mount Ararat; Mount Nisir; ancient Greece; ancient Greeks; Deucalion; Pyrrha of Thessaly; Plato (c.428 BC-c.348 BC); Timaeus; Ovid; Metamorphoses; Bronze Age; wife; Mount Parnassus; oracle; Greek mythology; goddess; Themis; bone; mother; Earth goddess; Mother Earth; rock (geology); man; woman; efficiency; efficienct; abiogenesis; prehistory; prehistoric times; theory; Thera eruption; Mediterranean Sea; meteorite; meteor; comet; Indian Ocean; mile; diameter; kilometer; Burckle Crater; Homo sapiens -anatomical modernity; modern humans; asteroid impact avoidance; detection and mitigation of potentially deadly asteroids; Invaders from Space (video game); artist; Bedout; northwestern coast of Australia; massive extinction; scientific literature; Science (journal); impact crater; Greenland Ice Sheet; scientist; research; University of Copenhagen (Copenhagen, Denmark); Aarhus University (Aarhus, Denmark); Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (Bremerhaven, Germany); University of California, Irvine (Irvine, California); NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (Pasadena, California); University of Bremen (Bremen, Germany); University of Alaska Fairbanks (Fairbanks, Alaska); Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (Copenhagen, Denmark); Maine Mineral and Gem Museum (Bethel, Maryland); University of Ottawa (Ottawa, Canada); Technical University of Denmark (Kongens Lyngby, Denmark); University of Fribourg (Fribourg, Switzerland); University of Zurich (Zurich, Switzerland); Cardiff University (Cardiff, UK); Université Grenoble Alpes (Grenoble, France); University of Kansas (Lawrence, Kansas); University of Cambridge (Cambridge, UK); Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (Cambridgeshire, UK); NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (Greenbelt, Maryland); Hiawatha Glacier; compass point name; northwest; Greenland; circle; circular; bedrock; asteroid; mammoth; North America; geochemistry; Geochemical analysis; sediment; iron; northern; survey; Wikimedia Commons; Eric Gaba; Solar System; chaos theory; chaotic; history; optimism; optimistic; conjecture; erosion; Moon; Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter; Tunguska event; energy; TNT equivalent; megatons of TNT; volcanic eruption; Krakatoa; volcano; explosion; P-wave; pressure wave; volcanic ash; temperature; Celsius; °C; weather; 1883 Krakatoa eruption; Royal Society of Great Britain; Houghton Library, Harvard University 71-1250; chronicle; 6th century; extreme weather events of 535-536; science; scientific; Byzantine Empire; Byzantine; historian; Procopius (c.500 - c.554); History of the Wars, Book IV, Chapter XIV; Europe; Middle East; Asia; mystery; mysterious; fog; growth ring; tree ring; climate; summer; decade; bubonic plague; Plague of Justinian; world population; Roman Empire; Paul Mayewski; colleague; Climate Change Institute; University of Maine (Orono, Maine); volcanic glass; particle; ice core; core drill; drilled; Colle Gnifetti Glacier; Swiss Alps; meter; atmospheric sediment; X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; elemental analysis by x ray excitation; XPS; Iceland; timeline; insolation; weather; crop failure; plague; Inkscape; society; lead; silver; smelting; Black Death; Y pestis.