Nano Copper Catalyst
April 16, 2012
Platinum is a great
catalyst. It has an active surface that allows
chemicals to overcome the
activation energy of
reactions, but it doesn't readily react with other chemicals, so its surface is always available. As an example, one of my
laboratory processes contained molten
lead oxide in a platinum
crucible, and the platinum was not
corroded.
Automotive catalytic converters mostly use platinum as a catalyst.
Oxidation, such as the
rusting of
iron, is a problem for most
metals, but one of my favorite
thermodynamics databooks [1] lists no platinum oxides. It does, however, list the two
copper oxides,
cuprous oxide (Cu
2O) and
cupric oxide (CuO). An example of copper oxidation and corrosion might be found in your pocket as a
penny. Copper reacts with the
oxygen in the air to form a protective, brown oxide; but it also reacts with
sulfides and other chemicals in the air, or on our hands, to form a corrosion product called a
patina.
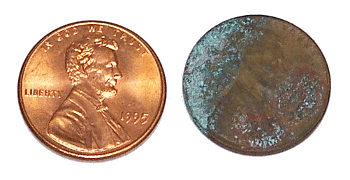
A 1995 US Penny (left), and a corroded 1944 US penny (right).
(Photo by author)
Copper is used a catalyst, but its catalytic capacity is usually diminished over time by reactions with other chemicals that reduce the number of catalytically active copper
atoms at the metal surface. The degradation process is called
poisoning, and I actually used poisoning to good advantage in preventing the decomposition of some
intermetallic hydrides.[2] Copper would be a fine catalyst for many reactions if poisoning could be controlled.
The reason why certain catalysts work better for some reactions than others is not well known, so it's usually best to stick with those that work, rather than trying to invent something new. Copper is a good catalyst for conversion of
carbon dioxide into
hydrocarbons, such as
methane. Since we're all wondering what we can do with the carbon dioxide thrown off in
electrical generation, a good copper catalyst might be a way to get rid of the carbon dioxide and produce fuel at the same time.[3] I reviewed one process for doing this using
solar-heated ceria ceramic in a
previous article (Solar Ceria, July 7, 2011).
A team of
MIT scientists has decided to tackle the copper catalyst poisoning problem using
nanotechnology. The team consists of
Kimberly Hamad-Schifferli, an associate professor of
mechanical engineering and
biological engineering,
Yang Shao-Horn, an MIT Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering,
postdoctoral associate, Zichuan Xu, and undergraduate, Erica Lai.[3]
Since previous research has shown that copper combined with
gold in bulk form prevented copper oxidation, the team decided to investigate nanoscale copper in gold.[3] Going to nanoscale has the added benefit that the
surface area of the catalyst is increased for the same
volume, potentially increasing
reaction rate and
yield. The nanoparticles were made by
evaporating a mixture of gold and copper
salts, then
reducing this to produce a metal powder by heating.[3]
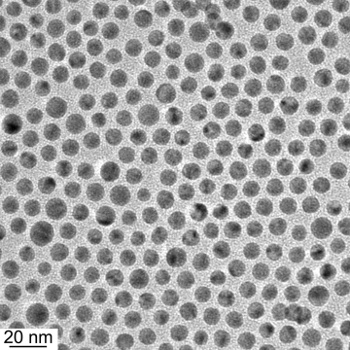
Electron micrograph of hybrid gold/copper nanoparticles.
Note the extremely small scale of the copper particles.
(MIT image by Zhichuan Xu))
The MIT team found that not that only a small quantity of gold was required for the copper to resist oxidation.
Electrodes for
electrochemical cells were coated with the nanoscale copper-gold powder.[3] The carbon dioxide reaction was performed by bubbling the gas into an electrochemical cell containing such electrodes.
The applied
voltage that was needed to attain a steady
current in such cells, which is indicative of a sustained reaction, was found to be much smaller for the nanocatalyst than for pure copper and gold.[3] If the catalyst were poisoned, the current at the reaction voltage would decrease as active sites were removed. Says Hamad-Schifferli,
"You normally have to put a lot of energy into converting carbon dioxide into something useful... We demonstrated hybrid copper-gold nanoparticles are much more stable, and have the potential to lower the energy you need for the reaction."[3]
Of course, an industrial-scale process of this sort for
carbon dioxide sequestration would require a lot of gold. It would be essential to go to the
spreadsheets and calculate the net benefit of this method of carbon sequestration, considering its fuel production capability and its potential for long life. After all, the gold isn't consumed, so its value is still there. Since there's a societal problem of people stealing copper, we had better add in the cost of armed guards!
A paper describing the catalyst will appear in the journal,
Chemical Communications. The research was funded by the
National Science Foundation.[3]
References:
- C. E. Wicks and F. E. Block, "Thermodynamic Properties of 65 Elements - Their Oxides, Halides, Carbides, and Nitrides," U. S. Bureau of Mines Bulletin 605, U. S. Government Printing Office (1963); Online version, via The University of North Texas Library; PDF version, via the University of Hawaii. My favorite is the the NIST-JANAF Thermochemical Tables, Fourth Edition, Monograph No. 9 (Part I and Part II, M.W. Chase, Jr., Editor), available from the American Institute of Physics, 2 Huntington Quadrangle, Melville, NY 11747-4502. A print version can be found on amazon, but NIST has an online database.
- D.M. Gualtieri, K.S.V.L. Narasimhan and T. Takeshita, "Control of the Hydrogen Absorption and Desorption of Rare Earth Intermetallic Compounds," J. Appl. Phys., vol. 47, no. 8 (August 1, 1976), pp. 3432-3435.
- Jennifer Chu, "Hybrid copper-gold nanoparticles convert CO2," MIT Press Release, April 11, 2012.
- Web site of the Hamad-Schifferli Group, Mechanical and Biological Engineering, MIT.
Permanent Link to this article
Linked Keywords: Platinum; catalyst; chemical compound; chemical; activation energy; chemical reaction; reaction; laboratory; lead oxide; crucible; corrosion; automotive; catalytic converter; oxide; oxidation; rust; iron; metal; thermodynamics; copper; cuprous oxide; cupric oxide; penny; oxygen; sulfide; patina; atom; catalyst poisoning; intermetallic; hydride; carbon dioxide; hydrocarbon; methane; electrical generation; solar thermal collector; ceria; ceramic; Massachusetts Institute of Technology; MIT; scientist; nanotechnology; Kimberly Hamad-Schifferli; mechanical engineering; biological engineering; Yang Shao-Horn; postdoctoral associate; gold; surface area; volume; reaction rate; yield; evaporation; salt; reduction; electrode; electrochemical cell; voltage; current; spreadsheet; Chemical Communications; National Science Foundation.